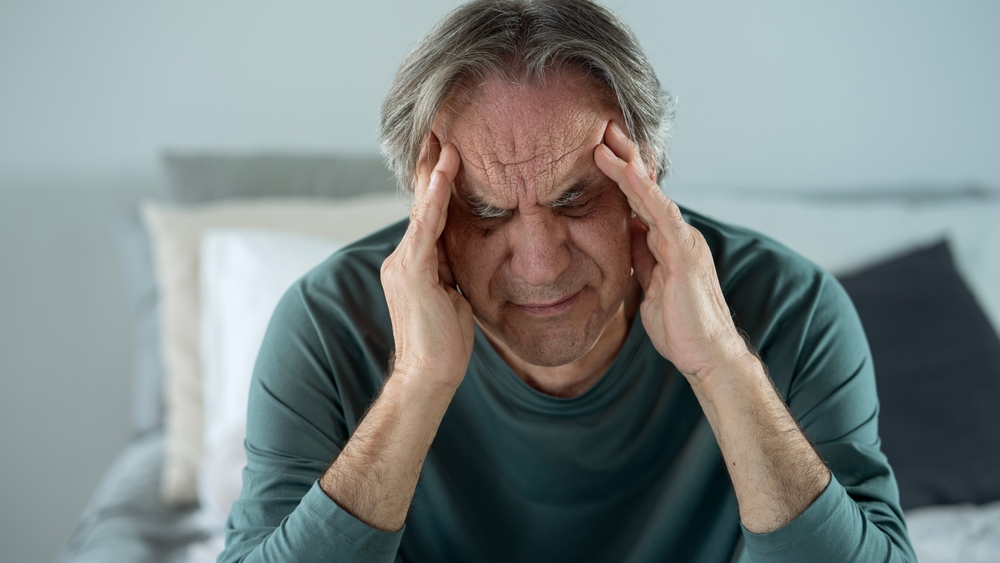
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) can have far-reaching effects on many aspects of daily life, including vision. While most people associate brain injuries with cognitive or motor impairments, the visual system is also frequently affected. This is because many of the brain's neural pathways are involved in processing visual information. When a brain injury occurs, these pathways can be disrupted, leading to a wide range of visual challenges that affect a person’s ability to function comfortably in daily activities.
The Brain’s Role in Vision
The brain plays a crucial role in vision, with multiple areas contributing to different aspects of sight and visual processing:
The occipital lobe (at the back of the brain) is primarily responsible for processing visual information.
The parietal lobe helps with spatial awareness and eye movements.
The temporal lobe assists in object recognition and visual memory.
The frontal lobe contributes to eye movement control and attention.
The brainstem and cerebellum play a role in coordinating eye movements and balance.
Because so many areas of the brain are involved in vision, a TBI can lead to a wide variety of visual symptoms and impairments.
Effects of Traumatic Brain Injury on Visual Skills
After a TBI, a person may experience difficulties with several important visual skills, including:
Focus (Accommodation): The ability to shift focus between near and far objects may be impaired, causing blurred vision, headaches, or difficulty reading.
Eye Alignment (Binocular Vision): Damage to the brain’s visual processing centers can cause double vision or difficulty coordinating both eyes together.
Tracking (Eye Movements): Smooth and accurate eye movements are essential for reading and following moving objects. A TBI can disrupt these functions, leading to problems with reading fluency and coordination.
Photophobia (Light Sensitivity): Many individuals with TBI experience extreme sensitivity to light, making it difficult to tolerate normal lighting or digital screens.
Visual Information Processing: The brain's ability to understand visual input may be impaired, leading to difficulties in understanding spatial relationships or remembering visual details.
Common Visual Symptoms After a Brain Injury
People who have suffered a TBI may experience a variety of visual symptoms, including:
Blurred or double vision
Sensitivity to light
Headaches or eye strain
Difficulty reading or comprehending written text
Trouble tracking moving objects
Poor depth perception
Increased difficulty with balance and coordination
Visual overwhelm
These symptoms can significantly impact reading, driving, working, and engaging in social interactions.
How Vision Therapy Can Help
Fortunately, vision therapy can help retrain and restore lost visual skills following a TBI. Vision therapy is a specialized, doctor-supervised program that involves exercises and techniques designed to strengthen the visual system. Some benefits of vision therapy for individuals with TBI include:
Improved Eye Coordination: Exercises can help the eyes work together more effectively, reducing symptoms like double vision.
Enhanced Tracking and Focus: Training can help restore smooth eye movements and the ability to shift focus between different distances.
Reduced Sensitivity to Light: Therapy can help patients gradually build tolerance to bright lights and screens.
Better Visual Processing Skills: Therapy helps retrain the brain to interpret and respond to visual information more efficiently.
Regaining Clear and Comfortable Vision
Recovering from a traumatic brain injury can be a long and challenging process, but addressing vision problems is a crucial step in regaining independence and quality of life. If you or someone you know has experienced visual difficulties following a TBI, a comprehensive eye exam with a doctor who specializes in neuro-optometric rehabilitation can help determine the best course of treatment.
Through targeted vision therapy, individuals can regain lost visual skills, improve comfort, and restore their ability to engage in everyday activities with confidence.